Outlet Flow Temperature Control in Heat Exchangers Using Q-Learning
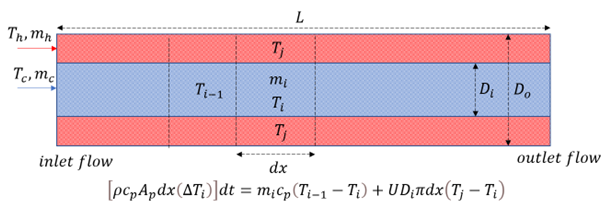
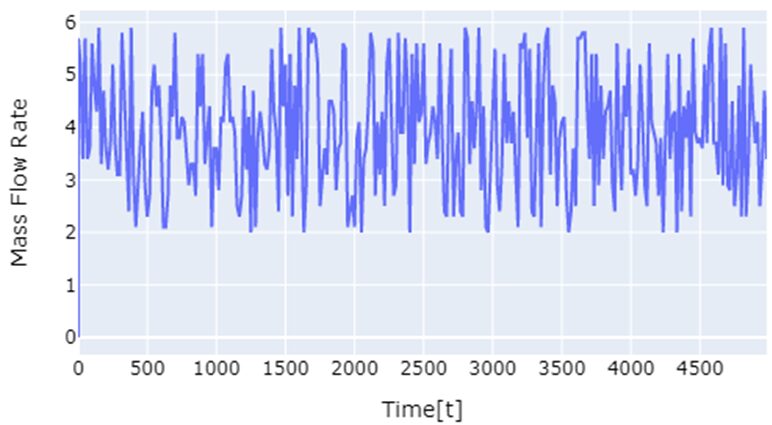
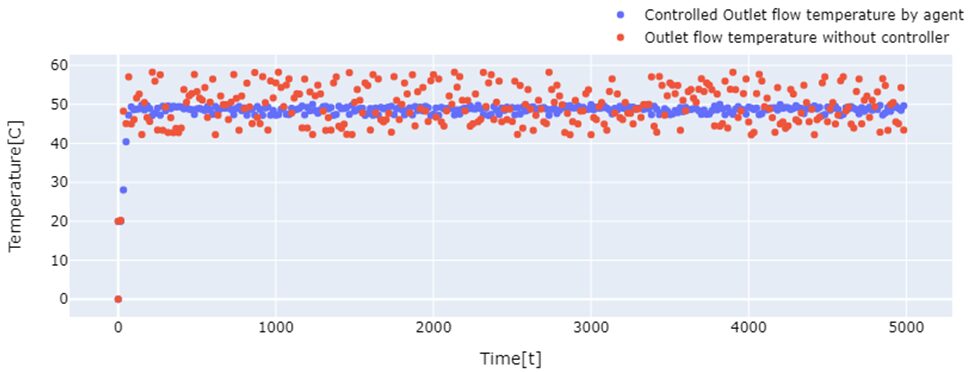
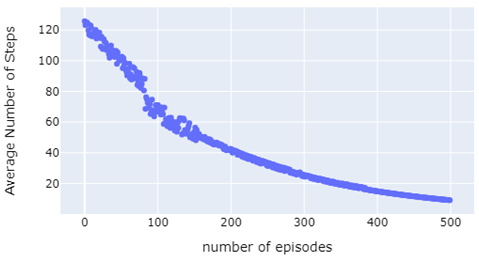
The project focuses on controlling outlet flow temperatures in heat exchangers, particularly under transient heat sources, using Reinforcement Learning (RL). The Q-learning algorithm is employed to regulate the outlet flow temperature of a co-current flow heat exchanger in dynamic situations.